Types of Memory Areas Allocated By the JVM
All these functions take different forms of memory structure. The memory in the JVM is divided into 5 different parts:
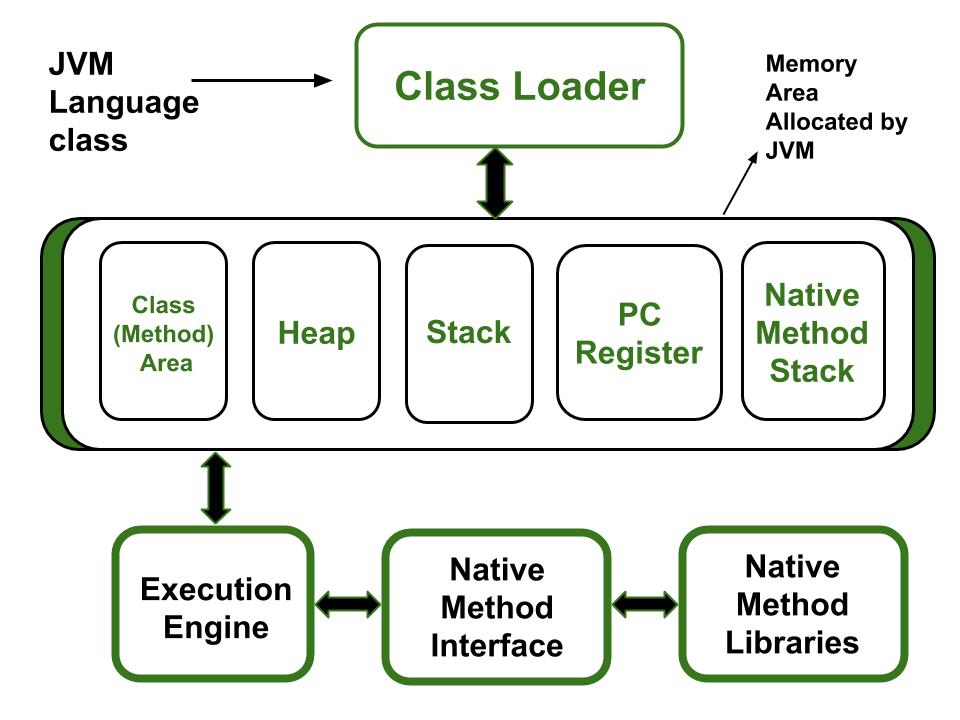
- Class(Method) Area
- Heap
- Stack
- Program Counter Register
- Native Method Stack
Let’s see about them in brief:
1. Class (Method) Area
The class method area is the memory block that stores the class code, variable code(static variable, runtime constant), method code, and the constructor of a Java program. (Here method means the function which is written inside the class). It stores class-level data of every class such as the runtime constant pool, field and method data, the code for methods.
2. Heap
The Heap area is the memory block where objects are created or objects are stored. Heap memory allocates memory for class interfaces and arrays (an array is an object). It is used to allocate memory to objects at run time.
Note: Static Methods and Variables were previous stored in Class Area (Till Java 8). But, in current versions of Java static variables and methods are stored in Heap Memory
The heap is divided into two generations: the Young Generation and the Old Generation (also known as the Tenured Generation).
Young Generation:
New objects are allocated in the Young Generation.
Further divided into the Eden space and two Survivor spaces (S0 and S1).
Objects surviving a certain number of garbage collection cycles are promoted to the Old Generation.
Old Generation (Tenured Generation):
Contains long-lived objects surviving numerous garbage collection cycles in the Young Generation.
Garbage collected less frequently compared to the Young Generation.
PermGen (Deprecated):
PermGen (Permanent Generation) was a special heap space separated from the main memory heap.
Used to store metadata about loaded classes, static content, bytecode, names, and JIT information.
Deprecated in Java 8 and removed in Java 8u20 and later versions due to issues like OutOfMemoryError.
MetaSpace:
Introduced in Java 8 to replace PermGen.
Stores metadata about classes, methods, and other runtime artifacts.
Unlike PermGen, MetaSpace's native memory region grows automatically by default.
Garbage collector automatically triggers the cleaning of dead classes once the class metadata usage reaches its maximum metaspace size, reducing the chance of OutOfMemory errors.
3. Stack
Each thread has a private JVM stack, created at the same time as the thread. It is used to store data and partial results which will be needed while returning value for method and performing dynamic linking.
Java Stack stores frames and a new frame is created each time at every invocation of the method. A frame is destroyed when its method invocation completes
4. Program Counter Register:
Each JVM thread that carries out the task of a specific method has a program counter register associated with it. The non-native method has a PC that stores the address of the available JVM instruction whereas, in a native method, the value of the program counter is undefined. PC register is capable of storing the return address or a native pointer on some specific platform.
5. Native method Stacks:
Also called C stacks, native method stacks are not written in Java language. This memory is allocated for each thread when it’s created And it can be of a fixed or dynamic nature.

Post a Comment