@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/", "/home").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login")
.permitAll()
.and()
.logout()
.permitAll();
}
}How does Spring Security integrate with Spring Boot applications?
Spring Security seamlessly integrates with Spring Boot applications through auto-configuration, which automatically applies security best practices by default. When Spring Security dependency is added to a Spring Boot application, it automatically configures a security model that is suitable for most needs. This integration simplifies securing web applications, APIs, and method-level security through annotations. Developers can further customize security settings to meet their specific requirements without having to write extensive configuration.
In a Spring Boot application, simply including the Spring Security dependency in your pom.xml or build.gradle file is enough to activate the default security settings. Further customizations can be added as needed.
What are the key components of Spring Security?
The key components of Spring Security include Authentication, Authorization, Principal, Granted Authority, and Filters.
Authentication is the process of verifying who a user is, while Authorization determines what an authenticated user is allowed to do. The Principal represents an entity (typically a user) within the application. Granted Authority refers to the permissions granted to the principal. Filters are used by Spring Security to intercept requests to enforce authentication and authorization.
Can you explain the role of the WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter in Spring Security?
The WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter is a convenience class provided by Spring Security that allows customization to both WebSecurity and HttpSecurity. Developers extend this class and override the relevant methods to configure aspects of web security such as configuring security realms, enabling CSRF protection, and controlling session management. It is the central place to configure web-based security for specific http requests.
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class CustomWebSecurityConfigurerAdapter extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.csrf().disable() // Disable CSRF protection as an example
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
.antMatchers("/user/**").hasRole("USER")
.antMatchers("/public/**").permitAll()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login")
.defaultSuccessUrl("/home")
.permitAll()
.and()
.logout()
.logoutSuccessUrl("/login?logout")
.permitAll();
}
}How does Spring Security handle authentication?
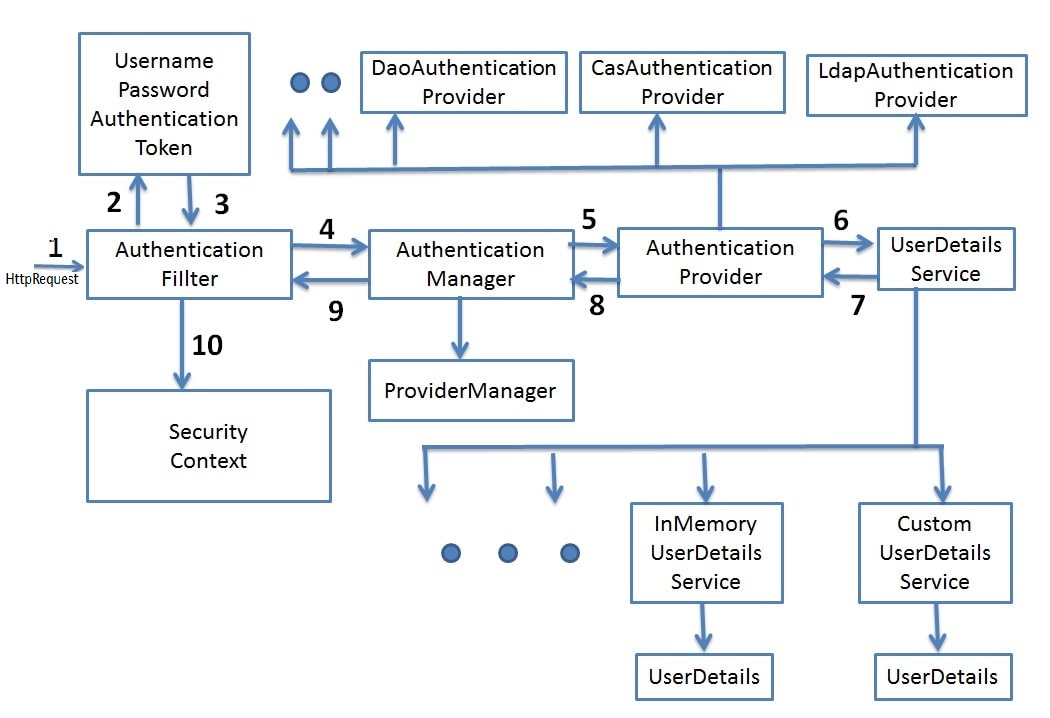
Spring Security handles authentication by verifying a user’s identity against provided credentials, typically a username and password combination. The process involves the AuthenticationManager interface, which delegates the actual authentication process to an AuthenticationProvider that checks the credentials against a source, such as a database, LDAP, in-memory storage, or other custom source. Upon successful authentication, a fully populated Authentication object, including the principal and granted authorities, is returned, signifying the user’s identity and roles.
@Component
public class CustomAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider {
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
String username = authentication.getName();
String password = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
// Here, add your logic to authenticate against a database, for example.
if ("user".equals(username) && "password".equals(password)) {
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password, Collections.emptyList());
} else {
throw new BadCredentialsException("Authentication failed for " + username);
}
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
return authentication.equals(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class);
}
}What is the difference between authentication and authorization in Spring Security?
@Service
public class TaskService {
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('ROLE_USER')")
public void executeUserTask() {
// Task logic for users
}
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('ROLE_ADMIN')")
public void executeAdminTask() {
// Task logic for admins
}
}@Service
public class MyUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
// Here, implement your logic to find the user by username from a database, for example.
if ("admin".equals(username)) {
return new User("admin", "password", Collections.singletonList(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_ADMIN")));
} else {
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("User not found with username: " + username);
}
}
}What is OAuth2 Authorization code grant type?
OAuth (Open Authorization) is a simple way to publish and interact with protected data.
- Authorization code grant
- Implicit grant
- Resource owner credentials grant
- Client credentials grant
- Refresh token grant
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.csrf().csrfTokenRepository(CookieCsrfTokenRepository.withHttpOnlyFalse())
.and()
.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated();
}
}This configuration enables CSRF protection with a cookie-based token repository.
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.sessionManagement()
.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)
.and()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/api/public/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/api/private/**").authenticated()
.and()
.addFilter(new JWTAuthenticationFilter(authenticationManager()));
}
} |
| Spring Security Overview |

Post a Comment