AtomicInteger
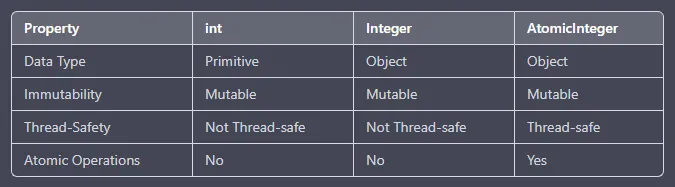
AtomicInteger are classes in the java.util.concurrent.atomic package. It provides atomic (thread-safe) operations on underlying int fields.
This class provides you with an int value that can be read and written atomically, and contains advanced atomic operations. Atomic operations are performed in a single unit of task without interference from other operations. AtomicInteger supports atomic operations on underlying int variables such as compareAndSet, decrementAndGet, incrementAndGet, etc.
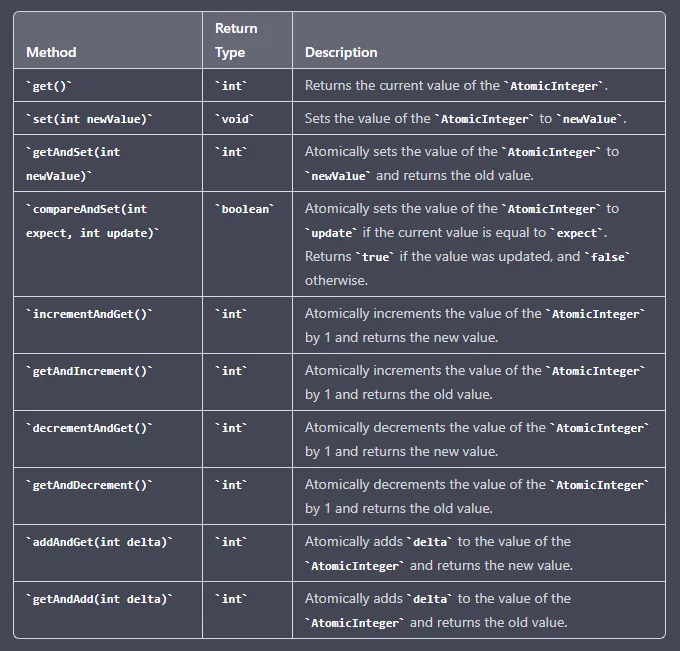
Let’s go through some of the key operations provided by the AtomicInteger class in Java.
get(): This method returns the current value.
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(5); System.out.println(atomicInteger.get()); // Output: 5set(int newValue): This method sets the value to the given updated value.
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(5); atomicInteger.set(10); System.out.println(atomicInteger.get()); // Output: 10getAndSet(int newValue): This method atomically sets the value to the given updated value and returns the old value.
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(5); System.out.println(atomicInteger.getAndSet(10)); // Output: 5 System.out.println(atomicInteger.get()); // Output: 10compareAndSet(int expect, int update): This method atomically sets the value to the given updated value if the current value equals the expected value.
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(5); System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(5, 10)); // Output: true System.out.println(atomicInteger.get()); // Output: 10getAndIncrement(): This method atomically increments the current value by one and returns the old value.
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(5); System.out.println(atomicInteger.getAndIncrement()); // Output: 5 System.out.println(atomicInteger.get()); // Output: 6getAndDecrement(): This method atomically decrements the current value by one and returns the old value.
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(5); System.out.println(atomicInteger.getAndDecrement()); // Output: 5 System.out.println(atomicInteger.get()); // Output: 4getAndAdd(int delta): This method atomically adds the given value to the current value and returns the old value.
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(5); System.out.println(atomicInteger.getAndAdd(5)); // Output: 5 System.out.println(atomicInteger.get()); // Output: 10incrementAndGet(): This method atomically increments the current value by one and returns the updated value.
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(5); System.out.println(atomicInteger.incrementAndGet()); // Output: 6decrementAndGet(): This method atomically decrements the current value by one and returns the updated value.
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(5); System.out.println(atomicInteger.decrementAndGet()); // Output: 4addAndGet(int delta): This method atomically adds the given value to the current value and returns the updated value.
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(5); System.out.println(atomicInteger.addAndGet(5)); // Output: 10

Post a Comment